Lemur
Get your space observation data in seconds
Whether you're tracking asteroids, monitoring satellites, or updating orbital catalogs, Lemur delivers fast, reliable results with minimal human intervention.
- Advanced Image Detection
- Astrometry + Photometry
- Catalog Cross-Matching
or
Already have an account? Login here




Trusted by



The information you need —
All in one environment
Turn raw telescope data into precise astrometric solutions
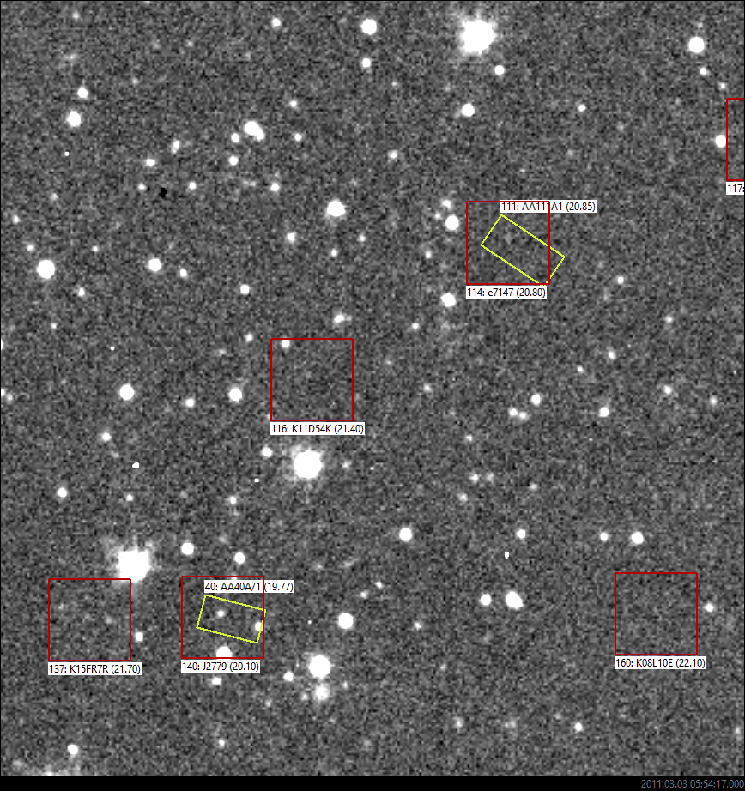
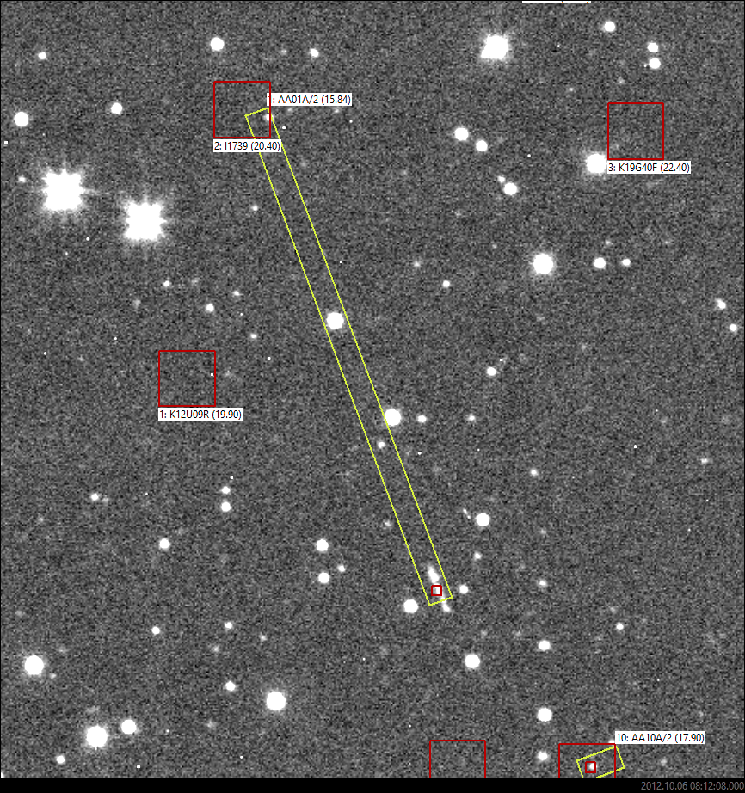
Detect, classify, and track LEO/MEO/GEO satellites, asteroids, and comets
Get information even under low signal-to-noise ratios with advanced image detection
Automatically reduce raw telescope data into precise, calibrated positions and brightness measurements for any tracked object
Fully automated
Space Domain Awareness
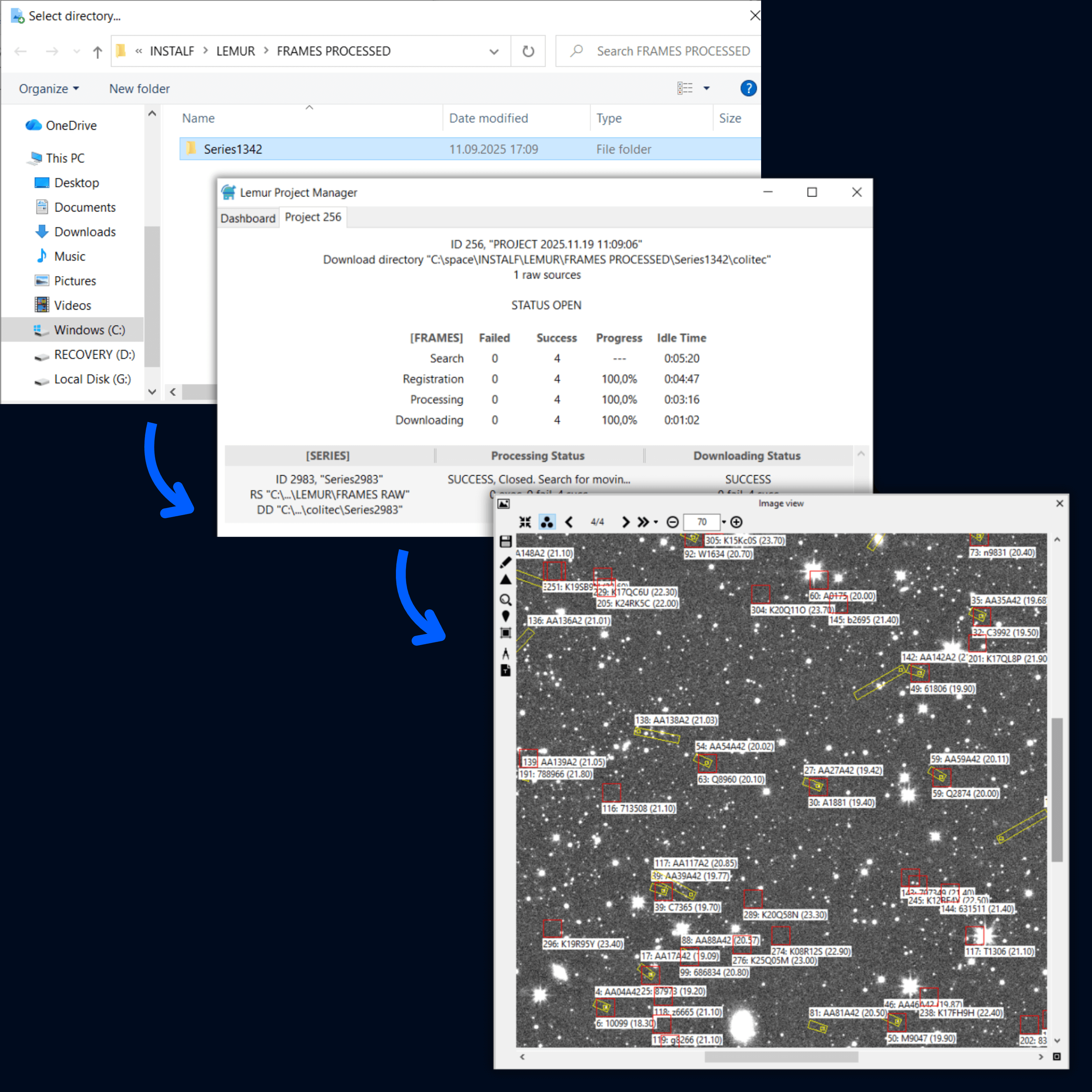
- Get information in four steps:
Upload → Process → Download → Visualize
- Process each 1920×1200
frame in seconds
- Recognize known objects
instantly via MPC & NORAD
From large observatories to
small research labs
Teams use Lemur to streamline space observation data collection and processing

Processing asteroid observation data from Baldone Observatory obtained with the Baldone Schmidt telescope with the Lemur program allowed me to reduce the time spent on routine pre-processing operations more than five times and focus on the scientific part of this work.

Dr.Phys. Ilgmars Eglitis
Head of Baldone Observatory Leading researcher of the Institute of Astronomy, University of Latvia

To conduct astrometric observations of geosynchronous objects at UzhNU’s lab, software was needed to process the images. The “Lemur” program handled this task excellently. With minimal adjustments to data collection, it was possible.

PhD, Kudak Viktor
Scientific Director of the Educational and Scientific Laboratoiy of the UzhNU
Ready to transform how you get your space observation data?
Get started with Lemur today — it's free

